Footnotes
The footnotes feature allows you to add supplementary information, citations, or explanatory notes that appear at the bottom of your document without cluttering the main text. Simply select any content you need annotated and click the footnote button to create a numbered reference that readers can easily navigate to and from.
Due to the differences between printed and digital content, the footnotes in CKEditor 5 are actually grouped together, like endnotes, and not at the bottom of each page.
Point your cursor to where you need to add a footnote and use the toolbar footnote button to add one. You can also edit existing footnotes and choose marker style by clicking in the footnotes area.
In number theory1, Fermat's Last Theorem2 (sometimes called Fermat's conjecture, especially in older texts) states that no three positive integers3 a, b, and c satisfy the equation an + bn = cn for any integer value of n greater than 2. The cases n = 1 and n = 2 have been known since antiquity to have infinitely many solutions.
-
^
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers4 and arithmetic functions.
-
^
There is more than one Fermat's Theorem:
- Fermat's Last Theorem, about integer solutions to an + bn = cn
- Fermat's little theorem, a property of prime numbers
- Fermat's theorem on sums of two squares, about primes expressible as a sum of squares
- Fermat's theorem (stationary points), about local maxima and minima of differentiable functions
- Fermat's principle, about the path taken by a ray of light
- Fermat polygonal number theorem, about expressing integers as a sum of polygonal numbers
- Fermat's right triangle theorem, about squares not being expressible as the difference of two fourth powers
-
^
An integer is the number zero, a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...).
-
^
See footnote 3
After installing the editor, add the feature to your plugin list and toolbar configuration:
import { ClassicEditor } from 'ckeditor5';
import { Footnotes, FootnotesProperties } from 'ckeditor5-premium-features';
ClassicEditor
.create( document.querySelector( '#editor' ), {
licenseKey: '<YOUR_LICENSE_KEY>',
plugins: [ Footnotes, FootnotesProperties, /* ... */ ],
toolbar: [ 'insertFootnote', /* ... */ ],
footnotes: {
multiBlock: false // Turn off the multi-block support (enabled by default).
}
} )
.then( /* ... */ )
.catch( /* ... */ );Please note that the FootnotesProperties plugin is optional. See the Configuration section for more details.
Read more about installing plugins and toolbar configuration.
To use this premium feature, you need to activate it with proper credentials. Refer to the License key and activation guide for details.
The footnotes feature can be configured using the footnotes.multiBlock option. By default, this option is set to true, allowing users to create footnotes that span multiple blocks of content. You can disable this feature by setting multiBlock to false in the editor configuration:
ClassicEditor
.create( document.querySelector( '#editor' ), {
footnotes: {
multiBlock: false // Default: true
}
} )
When multiBlock is set to true, users can add footnotes that span multiple blocks of content, such as paragraphs or list items. This allows for more complex annotations and references within the document.
When multiBlock is set to false, users can only add footnotes to single blocks of content. This is useful for simpler documents where footnotes are only needed for specific points within a block. The content of the footnote definition will be limited to text only.
The optional FootnotesProperties plugin (as seen imported in the Installation section) adds a contextual dropdown that appears when you click the footnotes definitions area. It provides quick access to footnote formatting options, allowing users to change the marker numbering style.
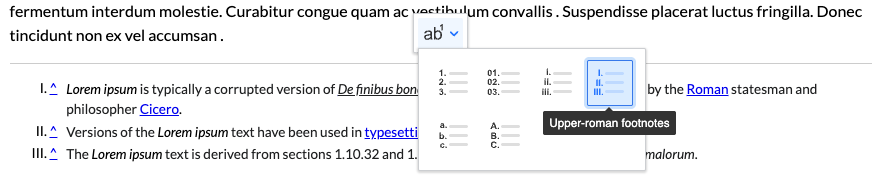
The FootnotesProperties plugin provides additional configuration option to choose the default style of the list item markers:
ClassicEditor
.create( document.querySelector( '#editor' ), {
footnotes: {
footnotesProperties: {
// The default footnotes list style for newly created footnotes lists.
// It can be changed using the 'Footnotes style' dropdown in the editor UI.
defaultListStyle: 'decimal', // Default: 'decimal'
// The starting index for the footnotes list numbering.
// It can be changed using the 'start' dropdown in the editor UI.
// Note: The starting index must be a positive integer greater or equal to 0.
defaultStartIndex: 1, // Default: 1
// Configuration of the footnotes style dropdown shown when the user clicks footnotes definitions list.
toolbar: [ 'footnotesStyle' ] // Default: [ 'footnotesStyle' ]
}
}
} )
Available list styles: 'decimal', 'decimal-leading-zero', 'lower-roman', 'upper-roman', 'lower-latin', 'upper-latin'.
Moving the footnotes list while Track Changes is enabled is not supported - a document can contain at most one footnotes list. As a workaround, temporarily disable track changes or accept/reject the relevant changes, then perform the move.
Check out also these CKEditor 5 features to gain better control over your content style and format:
- General HTML Support – Allows you to enable HTML features (elements, attributes, classes, styles) that are not explicitly supported by other dedicated CKEditor 5 plugins.
- Headings – Divide your content into sections.
- Page break – Divide your content into pages.
The Footnotes plugin registers:
- The
'insertFootnote'command. - The
'insertFootnote'UI component – a button to insert footnotes.
The FootnotesProperties plugin registers:
- The
'footnotesStyle'command. - The
'footnotesStyle'UI component – a dropdown to change footnotes numbering style.
You can insert a footnote programmatically by executing the command:
editor.execute( 'insertFootnote' );
You can also specify a custom footnote ID:
editor.execute( 'insertFootnote', { footnoteId: 'my-custom-footnote-id' } );
If the footnoteId parameter is not provided, a unique ID will be generated automatically. The footnote ID must be a non-empty string without spaces that does not start with a digit.
You can change the footnotes style by executing:
editor.execute( 'footnotesStyle', { value: 'lower-roman' } );
Available style values: 'decimal', 'decimal-leading-zero', 'lower-roman', 'upper-roman', 'lower-latin', 'upper-latin'.